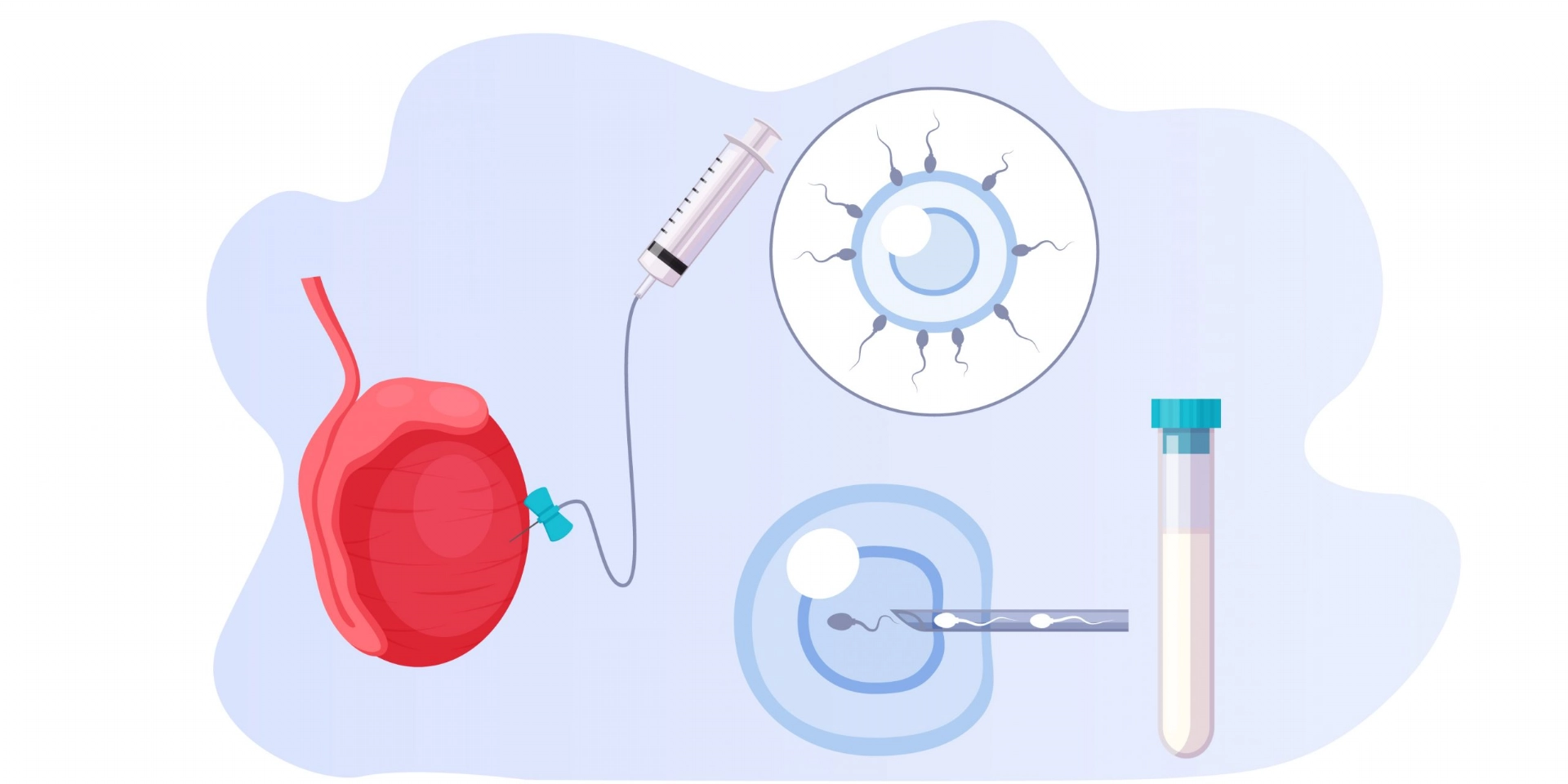
TESA/ TESE / Micro-TESE
 In some cases that cause azospermia in men, the problem can be solved by surgery. For example, in cases of blockages of reproductive channels or in cases of large varicocele, eliminating these problems can lead to reproduction. But today, instead of such surgical procedures, it is preferred to use methods of obtaining sperm from the testicle. If a man does not have any sperm in his semen sample (azoospermia), in this case, microinjection cannot be applied directly. Although sperm cannot be removed from the outside in men with this condition, there is a possibility of sperm being found in testicular tissue or in the ducts (epididymis) that store sperm. Urological examination and testicular tissue after various tests it to our patients to have sperm in the testis or sperm obtained from the channel or channels are the ones with the use of microinjection process can be successfully applied.
In some cases that cause azospermia in men, the problem can be solved by surgery. For example, in cases of blockages of reproductive channels or in cases of large varicocele, eliminating these problems can lead to reproduction. But today, instead of such surgical procedures, it is preferred to use methods of obtaining sperm from the testicle. If a man does not have any sperm in his semen sample (azoospermia), in this case, microinjection cannot be applied directly. Although sperm cannot be removed from the outside in men with this condition, there is a possibility of sperm being found in testicular tissue or in the ducts (epididymis) that store sperm. Urological examination and testicular tissue after various tests it to our patients to have sperm in the testis or sperm obtained from the channel or channels are the ones with the use of microinjection process can be successfully applied.
TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction) first applied in 1994; this method is the process of finding sperm from the testicles of azoospermic men who do not have any sperm in the semen sample. This process can also be done in men with total immotility in the whole semen sample. In couples who will undergo TESE procedure, the man is first taken to the surgery before oocytes are collected. Tissue samples taken from the testicles by the urologist under local or general anesthesia are sent to the laboratory to investigate whether there is sperm or not. If there is no sperm find, further tissue samples are continued to be taken until sperm is found or until it is determined that there is no sperm. Factors including the use of a surgical microscope (Micro-TESE) during the procedure, the experience and patience of the doctor performing the TESE procedure, and the removal of a sufficient number of parts increase the likelihood of finding sperm. If sperm is found, the woman’s eggs are collected and microinjection is performed. This method is called simultaneous TESE. If sperm is not found, the woman’s eggs are not collected and the treatment steps are terminated.

Alternatively, before preparing the female by ovulation induction step, only the male are undergo TESE procedure to investigate whether there is sperm or not, and if sperm is found, the tissue is stored by freezing and to use further . This process is called diagnostic TESE. After this stage, the woman enters the treatment cycle and ICSI is performed with thawed sperms. Here, the woman is not subjected to unnecessary treatment and stress if there is no sperm. The only and most important disadvantage of this practice is that a few frozen sperm can not be find during the process of thawing. For this reason, simultaneous and diagnostic TESE options should be clearly explained for the couple in detail with their advantages and disadvantages.
